 |
| Marie Curie was one of the first people to study radiation. |
Radiation
Review:
proton - positively charged particle
neutron - neutral particle, same mass as proton.
electrons - negatively charged, 1000 times lighter
Isotopes
- isotopes are two or more atoms that have the same number of protons, but different number of neutrons.
 |
| Isotopes of lithium. |
Notation:
Use this notation for each element, mass number and proton number.
Example: This is how you would write krypton with a mass of 78.
How many protons and neutrons does it have?
Answer: Protons = 36, Neutrons = 78 – 36 = 42
What is radiation?
- radiation is high energy particles or high energy electromagnetic waves
 |
| Small amounts of radiation can be used to diagnose diseases such as in a PET scan. |
 |
| Here's what a chunk of radioactive uranium looks like. |
Nuclear Radiation
- radiation emitted from an unstable nucleus.
- the original nucleus is the “parent”
- the products are called “daughters”
- there are three types: alpha, beta, and gamma
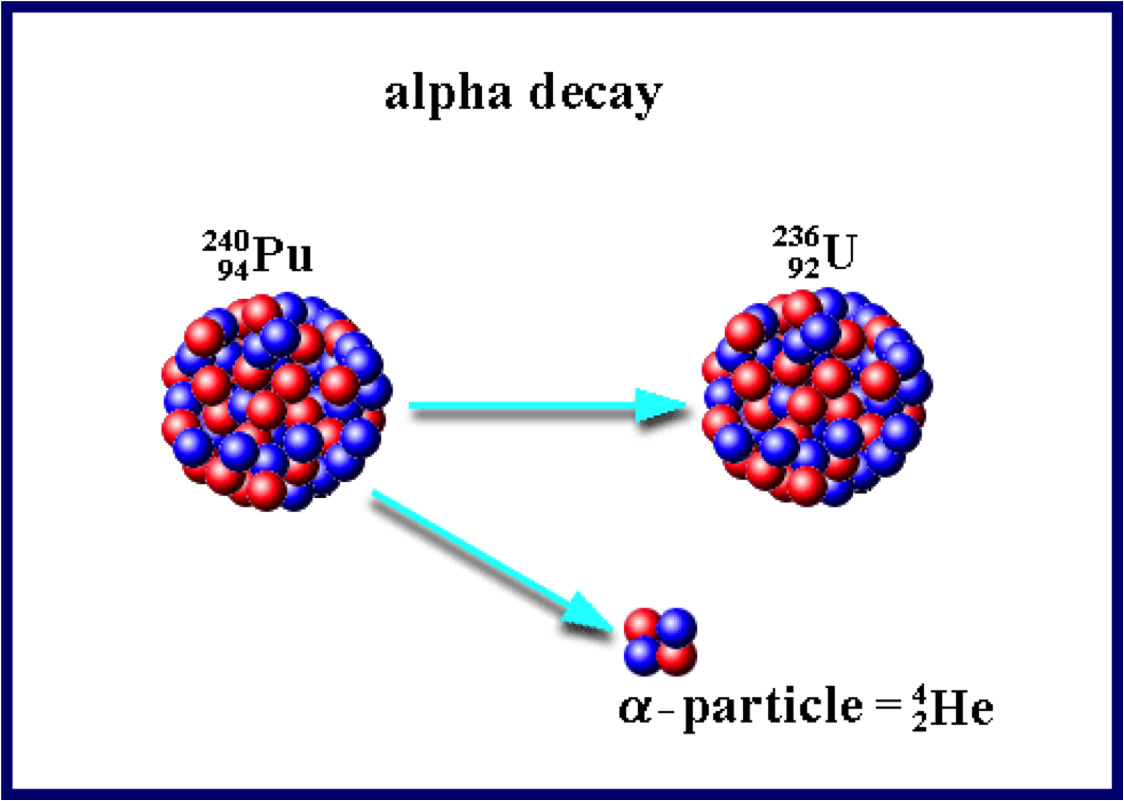
Alpha Decay
- an alpha particle consists of 2 protons and 2 neutrons (same as He nucleus)
- relatively large, easily stopped
- can penetrate a few cells into the body
Ex) Write the equation for Cu-64 undergoing alpha-decay.
Beta Decay
- A neutron decays into a proton, electron and anti-neutrino
- A beta particle is a high energy electron
- lighter and faster than alpha particles
- can be stopped by thin metal or plastic
Ex) Write the equation for Oxygen-19 undergoing beta-decay.
Gamma Decay
- A nucleus in an excited state loses energy and emits a photon
- A gamma particle is a high energy photon
Summary
Homework
- Please catch up on any homework you have not completed yet.






%2Bcopy.jpg)
-1.jpg)
No comments:
Post a Comment